Page Content
Kanban is a Japanese term means “visual board” or “sign”. It is a workflow management method for defining, managing, and improving services that deliver knowledge work. It aims to help you visualize your work, maximize efficiency, and improve continuously. Kanban was first developed and applied by Toyota in Japan as a scheduling system for just-in-time manufacturing.
Kanban Principles
• Change Management Principles
Start with what you do now. Respect current roles, responsibilities, and job titles.
Agree to pursue incremental, evolutionary change: Expect resistance to change.
Encourage acts of leadership at every level: Consider common feedback.
• Service Delivery Principles
Focus on the customer: Understand your customers’ needs and expectations.
Manage the work, not the individuals: Create an environment for individuals self-organize around it
Regularly review the network of services: Promote a culture of customer service.
Kanban Practices
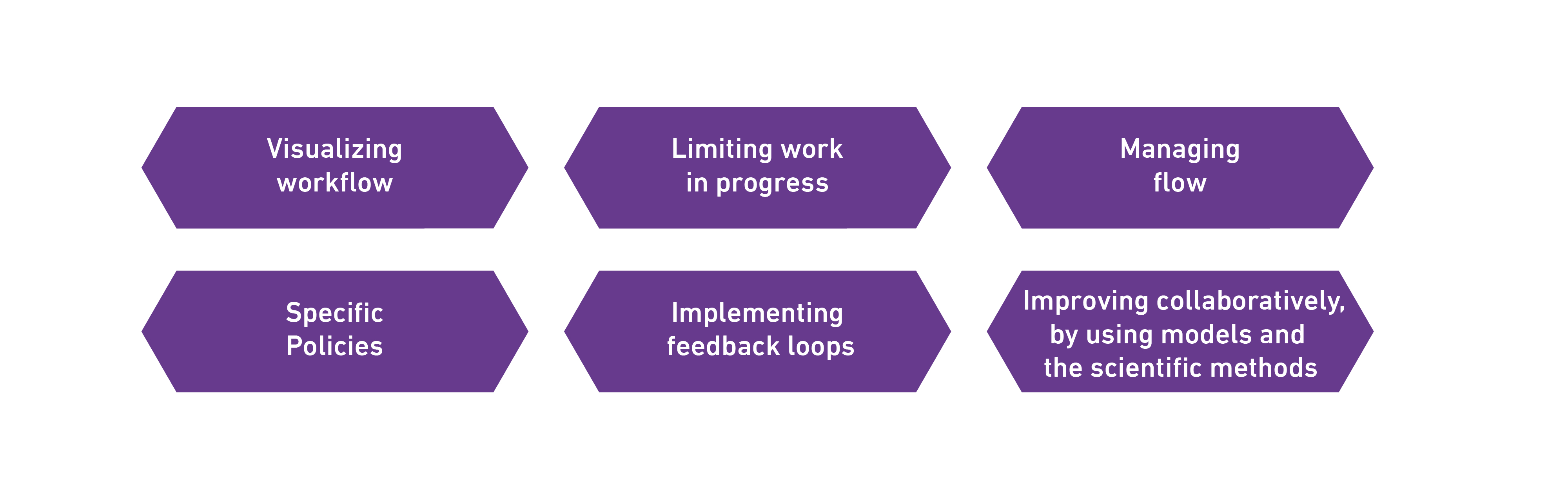
Best Practices for Agility with Kanban:
• Expanding Kanban approach within the organization
• Ensuring team leaders understand how the model works
• Enhancing horizontal driving
• Benefiting from customer feedback
• Increasing efficiency of tasks and practical steps
• Continuous improvement through scientific experiments
Updated Kanban Model
Kanban has evolved to keep pace with today's technology. Kanban's digital board is now used to overcome problems arising in remotely managed teams.